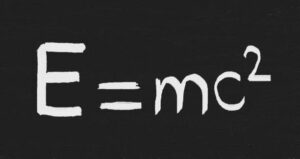Q NO 1: What is Gravitation? Write short introduction of Gravitation?
Introduction :
Table of Contents
ToggleEarth is part of Milky Way Galaxy , which is almost 100,000 light years in diameter . There are 200-400 billion stars in milky way galaxy . It consists of stars , gas and dust particles. Milky way galaxy is part of local group of Galaxies. There are hundreds of thousands progressively larger objects in the universe and all are moving in different orbits .
Gravitation:
The force which holds together all objects in the universe from moon to Galaxies and cluster is known as force of gravitation. Gravity is field force which acts even if objects are not in physical contact. This force not only holds our earth in milk way galaxy but have significance importance in various other operations.
Q No 2: If there is an attractive force between all objects, then why we don’t feel ourselves attracted towards each other and other objects?
Answer:
According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, all objects in the universe attract each other with a force known as force of gravitation. Both objects exert force of same magnitude on each other but these forces are opposite in direction. In other words we can say that these force follow Newton’s third law of motion. That is why we don’t feel ourselves attracted towards other objects.
Secondly,
The magnitude of the force between two objects is too small to detect . The force between a building of mass 10000 kg and 100 kg Person at a distance of 1 m will be 6.7×10-7 . So we don’t feel this force.
Q NO 3 : Earth is attracted by the sun, why it does not fall on the sun?
Answer:
Sun is a huge mass it attracts earth towards it with thousands Newton force following Newton’s law of universal gravitation. According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation , earth will exert force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on the sun. As both forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction so cancel effect of each other and neither the sun moves towards Earth nor the earth moves towards Sun.
Q NO 4 :How Newton’s law of Universal gravitation follows Newton’s third law of motion?
Answer:
In Newton’s third law of motion action and reaction forces act on each other. In Newton’s law of universal gravitation force acting on mass m1 due to mass m2 is F12. Also , force acting on mass m2 due to mass m1 is F21. These two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
F12 = -F21
We can say that these two forces action reaction forces because action reaction forces are also equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. So Newton’s law of universal gravitation follows Newton’s third law of motion.
Q NO 5 :What will be effect on gravitational force between two bodies if masses of both bodies are doubled?
Answer:
We know that , Newton’s law of universal gravitation is given by ,
F = Gm1m2 /r² ……. (i)
Now both masses are doubled, then m1‘ = 2m1 and m2‘ = 2m2.
Now , when both masses are doubled then the force will change this will be given by ,
F’ = Gm1‘m2‘/ r² …….. (ii)
Putting values of m1‘ and m2‘ in equation (ii)
F’ = G (2m12m2)/r²
F’ = G (4m1m2)/r²
F’ = 4 (Gm1m2) /r²
From equation (i) , F= Gm1m2 /r²
Putting values of F in equation (ii)
F’ = 4 F
which states that gravitational force will increase four times if both masses are doubled.
Q NO 6 :What will be effect on gravitational force between two bodies if distance is doubled?
Answer:
We know that , Newton’s law of universal gravitation is given by ,
F = Gm1m2/r² ……. (i)
Now if distance is doubled, then r’= 2r.
Now , if distance is doubled then the force will change this will be given by ,
F’ = Gm1m2/ r’² …….. (ii)
Putting value of r’ in equation (ii)
F’ = Gm1m2/(2r)²
F’ = Gm1m2/4r²
F’ = 1/4 (Gm1m2 /r²)
From equation (i) , F= Gm1m2/r²
Putting values of F in equation (ii)
F’ = 1/4 F
which states that gravitational force will decrease four times if distance between two masses is doubled.
Q NO 7 : What will be effect on gravitational force between two bodies if distance is halved?
Answer:
We know that , Newton’s law of universal gravitation is given by ,
F = Gm1m2/r² ……. (i)
Now if distance is halved, then r’= 1/2r.
Now , if distance is halved then the force will change this will be given by ,
F’ = Gm1m2/ r’² …….. (ii)
Putting value of r’ in equation (ii)
F’ = Gm1m2/(1/2r)²
F’ = Gm1m2/(1/4r²/
F’ = 4 (Gm1m2/r²)
From equation (i) , F= Gm1m2/r²
Putting values of F in equation (ii)
F’ = 4F
which states that gravitational force will increase four times if distance between two masses is halved.
Q NO 8 : What will be effect on gravitational force between two bodies if distance is tripled?
Answer:
We know that , Newton’s law of universal gravitation is given by ,
F = Gm1m2/r² ……. (i)
Now if distance is doubled, then r’= 3r.
Now , if distance is doubled then the force will change this will be given by ,
F’ = Gm1m2/ r’² …….. (ii)
Putting value of r’ in equation (ii)
F’ = Gm1m2/(3r)²
F’ = Gm1m2/9r²
F’ = 1/9 (Gm1m2 /r²)
From equation (i) , F= Gm1m2/r²
Putting values of F in equation (ii)
F’ = 1/9 F
which states that gravitational force will decrease nine times if distance between two masses is tripled.
Q NO 9 :What will be effect on gravitational force between two bodies if masses of both bodies are doubled and Distance is also doubled?
OR
Prove that there is no effect on gravitational force if both masses are doubled and distance is also doubled?
Answer:
We know that , Newton’s law of universal gravitation is given by ,
F = Gm1m2 /r² ……. (i)
Now both masses are doubled, then m1‘ = 2m1 and m2‘ = 2m2.
As distance is also doubled so r’ = 2r.
Now , when both masses are doubled and distance is also doubled then the force will change this will be given by ,
F’ = Gm1‘m2‘/ r’² …….. (ii)
Putting values of m1‘ and m2‘ and r’ in equation (ii)
F’ = G (2m12m2)/(2r²)
F’ = G (4m1m2/4r²)
F’ = 4/4 (Gm1m2/r²)
F’= Gm1m2/r²
Putting values of F in equation (ii)
F’ = F
which states that gravitational force will remain constant if both masses are doubled and distance is also doubled.
Q NO 10 :Show that N/kg is also unit of acceleration and equivalent to ms-2 ?
Answer:
The unit of acceleration is ms-2.
Unit of acceleration = ms-2
We can multiply and divide kg here in the equation,
Unit of acceleration = kgms-2/ kg
As kgms-2 is equal to Newton. So
Unit of acceleration= N / kg
Q NO 11 : If the radius of mercury is 2.4 × 10⁶ m and acceleration due to gravity is 3.7 m/s². Find the Mass of Mercury.
Given Data : Required:
Radius of Mercury = rm= 2.4 × 10⁶ m Mass of Mercury= Mm= ?
Acceleration due to gravity = gm= 3.7 N/kg
Gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm²/Kg²
Solution:
We can find Mass of any astronomical object with the help of this formula.
Mm= gmRm²/ G
Putting values
Mj = 3.7 Nkg-1 × (2.4 × 10⁶m)² / (6.67 × 10-11 Nm²kg-2)
Mj = 3.3 × 10²³ Kg
Q NO 12 : Why gravity is a field force?
Answer :
Newton was not able to explain how objects exert force on each other without coming in contact. Scientist developed a theory which states that masses create gravitational field around them . When another masss comes in the gravitational field of this mass ,this mass can exert force of gravity on that mass . In case of gravity the physical contact of bodies is not necessary, so gravity is a field force not a contact force.
Q NO 13 : What is difference between gravitational field strength and free fall acceleration?
Answer:
When an object falls freely it’s acceleration in given by ,
a= F/m
Also , gravitational field strength g is given by,
g = Fg/m
Where , Fg is gravitational force. Thus , value of gravitational field strength g is equal to acceleration due to gravity. Although gravitational field strength and gravitational acceleration are equivalent they are not the same thing .
Example :
When we hang in object from spring balance, we are measuring its gravitational field strength g , because object is address and their is no measurable acceleration. When it is falling freely , we can measure both its gravitational field strength and gravitational acceleration.
Q NO 14 : What will be affect on the value of g if mass of Earth is doubled?
We know that value of g at the surface of earth is given by ,
g = GME/Re² …… (i)
Now if mass of earth is doubled ,
ME‘ = 2ME
Then value of g also changes ,
g’ = GME‘ / RE² ……. (ii)
Putting value of ME’ in equation (ii)
g’ = G(2ME/RE²)
g’ = 2 GME/RE²
g’ = 2 g
Thus the value of g is doubled if mass of Earth is doubled.
Q NO 15 : What will be affect on the value of g if mass of Earth is halved?
Answer :
We know that value of g at the surface of earth is given by ,
g = GMe/Re² …… (i)
Now if mass of earth is halved ,
Me’ = 1/2Me
Then value of g also changes ,
g’ = GMe’ / Re² ……. (ii)
Putting value of Me’ in equation (ii)
g’ = G(1/2Me/Re²)
g’ = 1/2 GMe/Re²
g’ = 1/2 g
Thus the value of g is halved if mass of Earth is halved.
Q NO 16 : What will be affect on the value of g if radius of Earth is doubled?
We know that value of g at the surface of earth is given by ,
g = GMe/Re² …… (i)
Now if radius of earth is doubled ,
Re’ = 2Re
Then value of g also changes ,
g’ = GMe / Re’² ……. (ii)
Putting value of Re’ in equation (ii)
g’ = G(Me/(2Re)²
g’ = GMe/ 4Re²
g’ = 1/4 GMe/Re²
g’ = 1/4 g
Thus the value of g is decreases four times if radius of Earth is doubled.
Q NO 17 : What will be affect on the value of g if radius of Earth is halved?
Answer :
We know that value of g at the surface of earth is given by ,
g = GMe/Re² …… (i)
Now if radius of earth is halved ,
Re’ = 1/2Re
Then value of g also changes ,
g’ = GMe / Re’² ……. (ii)
Putting value of Re’ in equation (ii)
g’ = G(Me/(1/2Re)²
g’ = GMe/ (1/4Re²)
g’ = 1/4 GMe/ Re²
g’ = 1/4 g
Thus the value of g is decreases four times if radius of Earth is doubled.
Q NO 18 : What is free fall acceleration at the surface of Mars? As mass of Mars is 1.99 × 10³⁰ kg and it’s radius is 6.96× 10⁸ m?
Given data : Required:
Mass of sun = Ms = 1.99 × 10³⁰ Kg Value of g on Sun= gs = ?
Radius of sun = Re = 6.96 × 10⁸ m
Gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10-11Nm²/ kg²
Solution:
The value of g at surface of sun is given by ,
gs = GMs/ Rs²
Putting values ,
gs = 6.67×10-11Nm²/kg² × 1.99×10³⁰ Kg / (6.96×10⁸m)²
gs= 274 m/s²
Q NO 19 : At what altitude above earth the value of gravitational acceleration will be 4.9ms-2?
We know that , the value of gravitational acceleration at any point on height is
gh= geRe²/ (Re+h)² ….. (a)
gh × (Re+h)² = geRe²
(Re+h)² = geRe² / gh
√(Re+h)² = √(geRe² /gh)
Re+h = √(geRe² / gh)
h = √( geRe²/ gh ) – Re ……. (b)
Putting values ,
h = {√ (9.8ms-2 × (6.4×10⁶m )² / 4.9ms-2) – (6.4×10⁶m)
h = 2.6 × 10⁶ m
Q NO 20 : What keeps satellites moving around Earth?
Answer:
A satellite is put into orbit of Earth by brining it to a specific height and moving it with specific speed . High speed of Satellite keeps it moving around earth . If speed is too greater , Satellite will escape the earth . If it is too slow it will fall towards earth . Only a specific speed keeps it moving around Earth due to Earth’s gravitational force .
Q NO 21 : What will be affect on the speed of Satellite if its distance from centre of Earth is increased four times?
Answer :
We know that speed of Satellite is given by,
v = √GMe/R …… (i)
Now if it’s distance from centre of earth is increased four times ,
R’ = 4R
Then speed of Satellite also changes ,
v’ = √GMe / R’ ……. (ii)
Putting value of Re’ in equation (ii)
v’ = √GMe/4R
v’ = √1/4 (√ GMe/R)
v’ = 1/2 (√GMe/ R)
v’ = 1/2 v
Thus the speed of Satellite is halved if distance of Satellite from centre of earth is increased four times.
Q NO 22 : What will be affect on the speed of Satellite if its distance from centre of Earth is decreased four times?
Answer :
We know that speed of Satellite is given by,
v = √GMe/R …… (i)
Now if it’s distance from centre of earth is decreased four times ,
R’ = 1/4R
Then speed of Satellite also changes ,
v’ = √GMe / (1/4R) ……. (ii)
Putting value of Re’ in equation (ii)
v’ = √4GMe/R
v’ = √4 (√ GMe/R)
v’ = 2 (√GMe/ R)
v’ = 2 v
Thus the speed of Satellite is doubled if distance of Satellite from centre of earth is decreased four times.
Q NO 23 : What will be affect on the speed of Satellite if mass of earth is doubled?
Answer :
We know that speed of Satellite is given by,
v = √GMe/R …… (i)
Now if mass of earth is doubled,
Me’ = 2Me
Then speed of Satellite also changes ,
v’ = √GMe’ / R ……. (ii)
Putting value of Me’ in equation (ii)
v’ = √G2Me/ R
v’ = √2(√ GMe/R)
v’ = √2 (√GMe/ R)
v’ = √2 v
Thus the speed of Satellite is increased √2 times if mass of earth is doubled.
Q NO 24 : What will be effect on speed of Satellite if mass of Satellite is doubled?
Answer :
We know that speed of Satellite is given by,
v = √GMe/R …… (i)
The above equation shows that speed of satellite does not depend on mass of satellite. So if mass of satellite is doubled there is no effect on speed of satellite.
Q NO 25 : Geostationary satellites are placed in circular orbit that is 3.59×10⁶ m above the surface of earth. Calculate their orbital speed.
Solution:
As we know that the speed of satellite is given by ,
v = √GMe/ Re+h
v = √ 6.67×10-11Nm²kg-2× 6×10²⁴ kg / {(6.4×10⁶ m + 35.9×10⁶)}
v = 3.07 × 10³ m/s
v = 3.07 kms-1